In this article, we will read about Universe and Solar system Planets information. This is the first article of your Geomorphology course for Geography Optional UPSC aspirants.
UNIVERSE
- Everything that exists, from the Galactic Mega clusters to the tiniest subatomic particles, comprises the Universe.
- As for the age of the Universe, scientists agree that it is about 13.79 billion years old as 2015.
- The universe comprises of a number of galaxies.
- Optical and radio telescope studies indicate the existence of about 100 billion galaxies in the visible universe.
- The Big Bang Theory is most acceptable for the origin of the Universe.


GALAXY
- Galaxy is a collection of millions or billions of stars and planets that are held together by gravitational pull.
- Milky Way is one such galaxy. The earth lies in this galaxy. It is called Milky Way because it looks like a river of milky light flowing from one corner to another of the sky.
- It is spiral in shape.
- We call it Akash Ganga.
- The nearest galaxy to Milky Way is Andromeda.
- Andromeda is a spiral galaxy and approximately 2.5 million light-years from the earth.

STARS
- Luminous heavenly bodies which have their own light and other radiant energy are called a star.
- They are made of extremely hot burning gases.
- Star reflects Looks – Red with low temperature, Yellow with higher and blue with very high temperature.
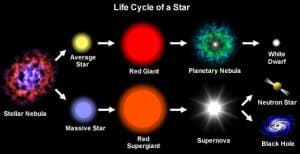
Star (Birth to Death)
- Star starts its life as clouds of dust and gas known as Nebula.
- The gaseous matter of Nebula further contracts to make dense region named ProtoStar.
- The ProtoStar further condenses to a critical stage of mass where nuclear fusion begins and star finally comes into existence.
- When all the hydrogens of a star are used up then its helium begins fusing into carbon. At a stage helium’s fusion and energy production inside the star stops. As a result, stars core contracts under its own weight to a very high density to make a white Dwarf star.
- A white Dwarf star becomes dark balls of matter on cooling to make Black Dwarf Star.
- The mass of white Dwarf Star is less than 1.44 times the mass of the Sun named as Chandrasekhar Limiting Mass.
- White Dwarf Star is a dead star because of the end of fusion reaction and energy production.
- It shines by radiating its stored heat.
- The giant star expands into Red Supergiant after consuming its fuel (H & He). At a stage, it explodes as Supernova or changes into Neutron or Black Holes.
- The nearest star to the Earth is the Sun followed by Proxima and Alpha Centauri and radiant energy. (4.35 Light years)
Constellations
- A Constellation is a group of stars that makes an imaginary shape in the sky at night.
- It helps in navigation of sea vessel during the night as they are seen in a fixed direction at a particular period of time in a year.
- Orian, Big Dipper, Great Bear, Cassiopeia are some examples of constellations.
- Orion or Mriga can be seen in the late evening during winter; Cassiopeia in the Northern Sky is seen during winter.
- Great Bear consists of Ursa Minor (Laghu Saptarishi) and Ursa Major (Vrihat Saptarishi) and can be seen in the early night during summer.