In this article, You will read Classification of the Indian Rocks i.e. Indian Rock System (Archaean, Purana, Dravidian & Aryan Rock System) – for UPSC IAS.
Contents
- Indian Rock System
The geological structure of a country helps in understanding the types and character of rocks and slopes, the physical and chemical properties of soils, the availability of minerals, and the surface and underground water resources.
Indian Rock System
- Geological Structure: Geological structure is most commonly (and best applied ) to the arrangements and deposition of the rocks in the earth’s crust, as a result of (or absence of) earth movements; but also applied to the morphological features (morphology) of rocks; e.g. Gondwana structure.
- Geological Time Scale: Chronological dating of various geological formations (Geological strata) and life according to their time and place of origin, evolution, and extinction. “Giovanni Ardunia developed Geological Time Scale in 1760”. Standard Geological Time Scale developed in International Geological Congress held in 1881, Italy.
- The Indian Geological Time Scale, advocated by T.S. Holland.
- Geological History of India: The Geological Structure & rock systems of India analyzed with reference to their geographical locations and their geological history. The following physiographic divisions of India are used for referencing the geological formations:
- Peninsular India;
- Extra Peninsular India
- Major events in the geological history of India:
- Peninsular India was a part of the old landmass since the formation of the Earth’s Crust
- The upheaval of the Himalayas in the tertiary period.
- Aggradational formation of the Indo-Gangetic plain during the Pleistocene period. It continues till today through sedimentation in the floodplains of the rivers and the lower part of the Gangetic plain.
Based on this complex and varied geological history, the Geological Survey of India has classified rock systems of the country into 4 major divisions:
- The Archaean Rock System
- The Purana Rock System
- The Dravidian Rock System
- The Aryan Rock System
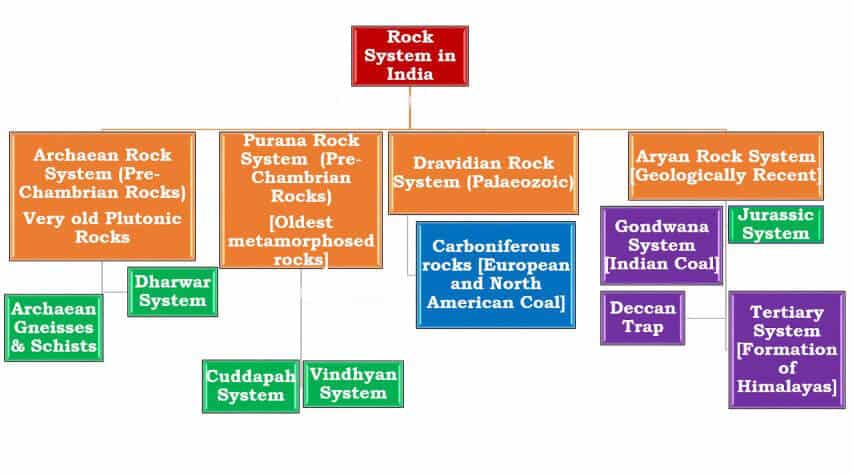
Archaean Rock System (Pre-Cambrian Rocks)
- The earliest phase of tectonic evolution was marked by the cooling and solidification of the upper crust of the earth’s surface in the Archaean era (prior to 2.5 billion years; Precambrian Period) which is represented by the exposure of gneisses and granites, especially on the Peninsula.
- These form the core of the Indian Craton (Block of Indian Subcontinent of Gondwanaland).
- The term ‘Archaean’ introduced by J.D. Dana in 1782, refers to the oldest rocks of the earth’s crust.
- The Archaean group of rocks consists of two systems-
- (a) Achaean System: Granites and Gneisses,
- (b) Dharwar System: First Sedimentary Rocks
Gneiss — Mineral composition varies from granite to gabbro.
Schists — mostly crystalline, include mica, talc, hornblende, chlorite, etc.