Asia
Asia is the world largest continent, having an area of 44,444,100 sq km.
It covers about 30% of Earth’s total land area and 8.7% of the Earth’s total surface area. with a population of 4.4 billion which is 60 % of the world’s total population.
It is a continent of contrast in relief, temperature, vegetation and people also.
Asia is to the east of the Suez Canal, the Ural River, and the Ural Mountains, and south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black Seas.
It is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean and on the north by the Arctic Ocean.
The earth’s highest and lowest places are both in Asia:
- The highest place on earth: Mount Everest
- The lowest place on earth: Dead Seashore
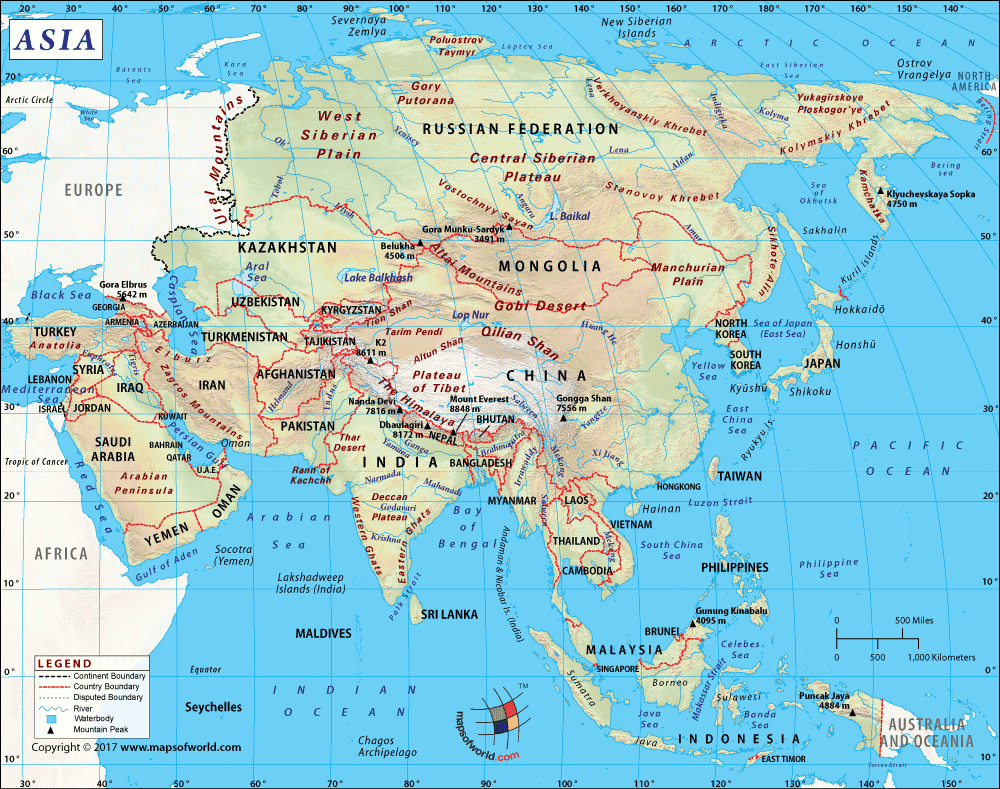
Regional Divisions of Asia
Asia can be divided into six physiographic divisions:
Central Asia: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan
Eastern Asia: China, Hong Kong, Japan, North Korea, South Korea, Macau, Mongolia, Taiwan
Northern Asia: Russia
South-eastern Asia: Brunei, Myanmar, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Timor-Leste, Vietnam.
Southern Asia: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka.
Western Asia: Armenia, Azerbaijana, Bahrain, Cyprus, Georgia, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, State of Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, Yemen.
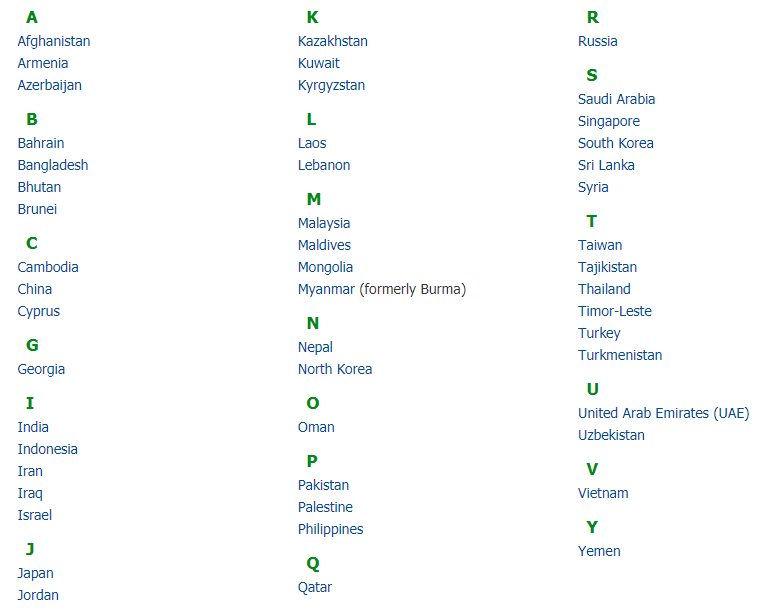
Major Physical Divisions of Asia
- The Northern Lowlands
- The Central Mountains
- The Central and Southern Plateaus
- The Peninsulas
- Deserts
- The Great River Plains
- Island Groups
1. The Northern Lowlands
The Northern Lowlands are the extensive plain areas that comprise of several patches of lowlands of this large continent.
The major lowlands are:
Great Siberian plain
- It extends between the Ural Mountains in the west and the river Lena in the east. It is the largest lowland in the world covering an area of 1,200,000 square miles approx.
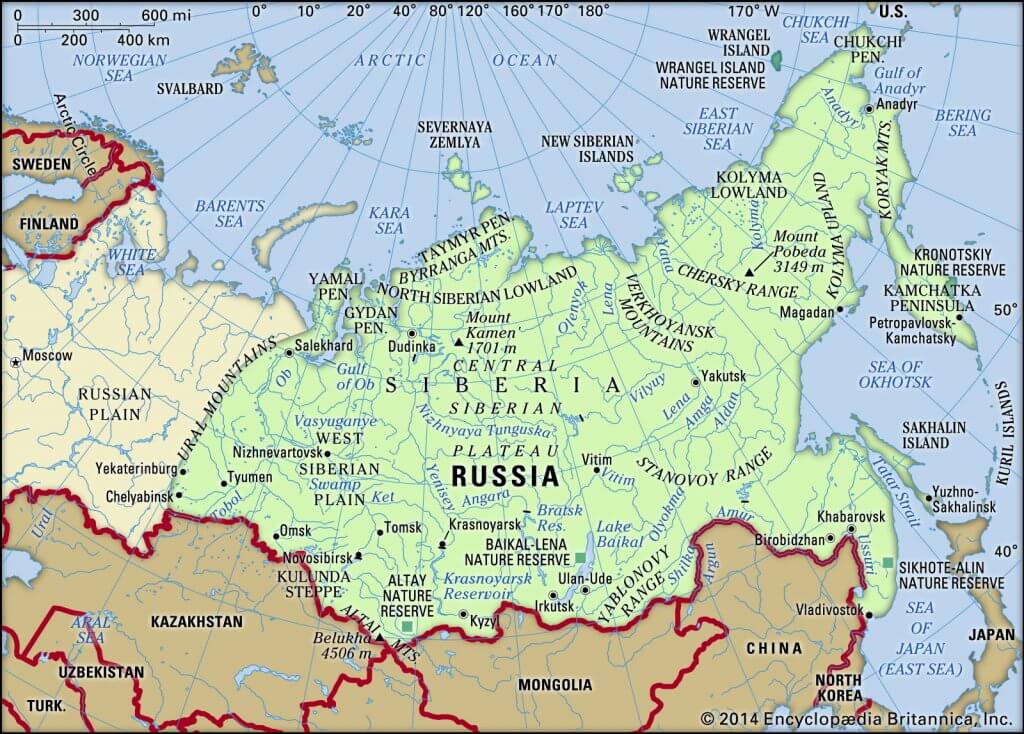
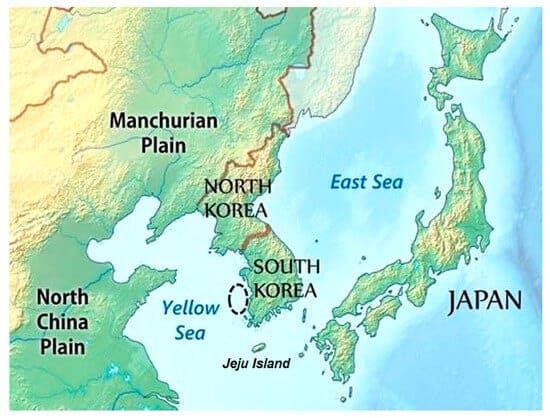
Manchurian Plain
- It is the area adjoining Amur river and its tributaries of the northern part of China with an area of 135,000 square miles approx.
Great Plains of China
- It is contributed by two major rivers of China, Hwang Ho and Yangtze river which covers an area of 158,000 square miles approx.
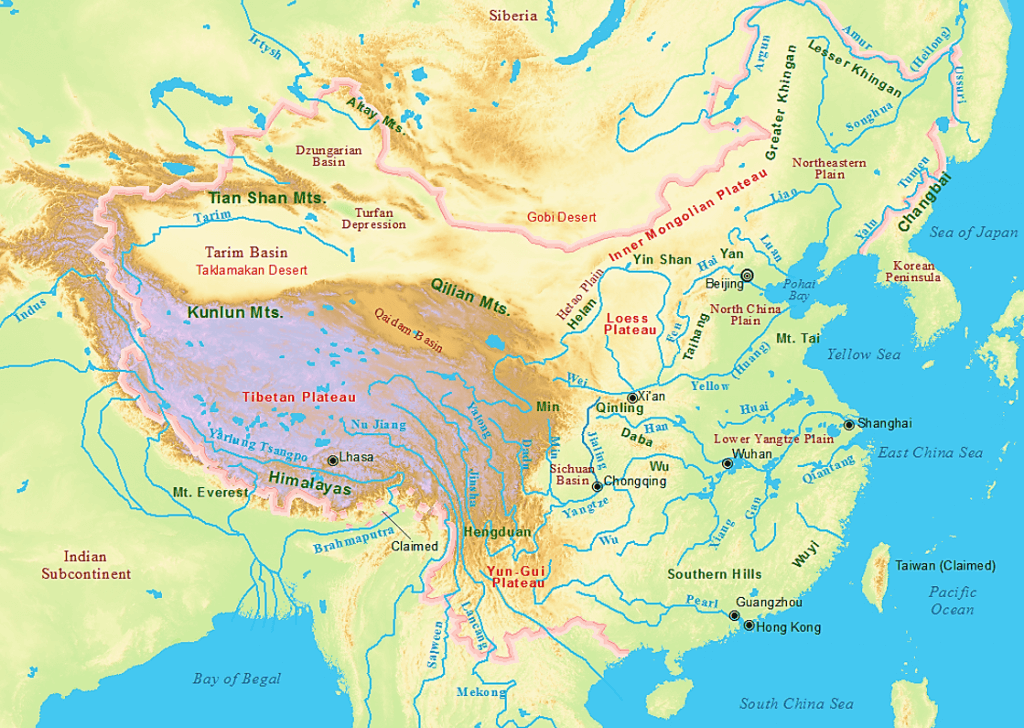
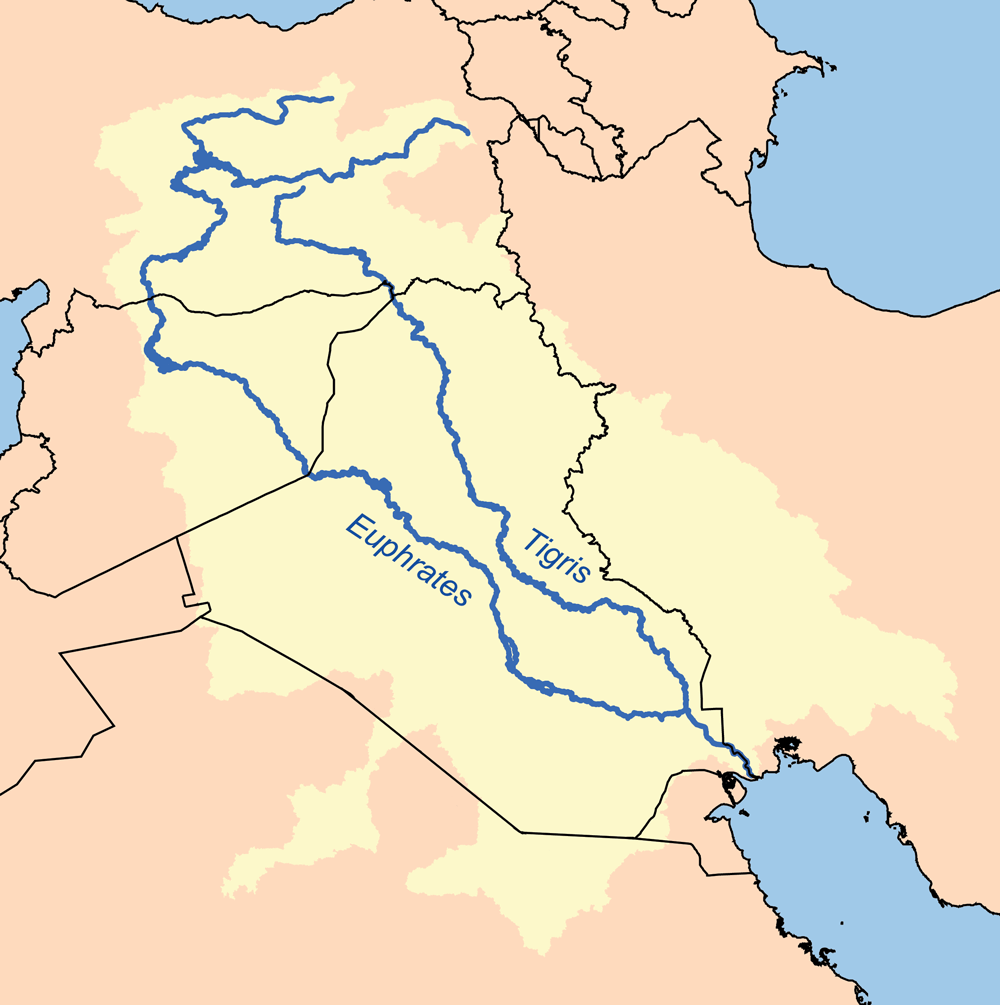
Tigris-Euphrates plains
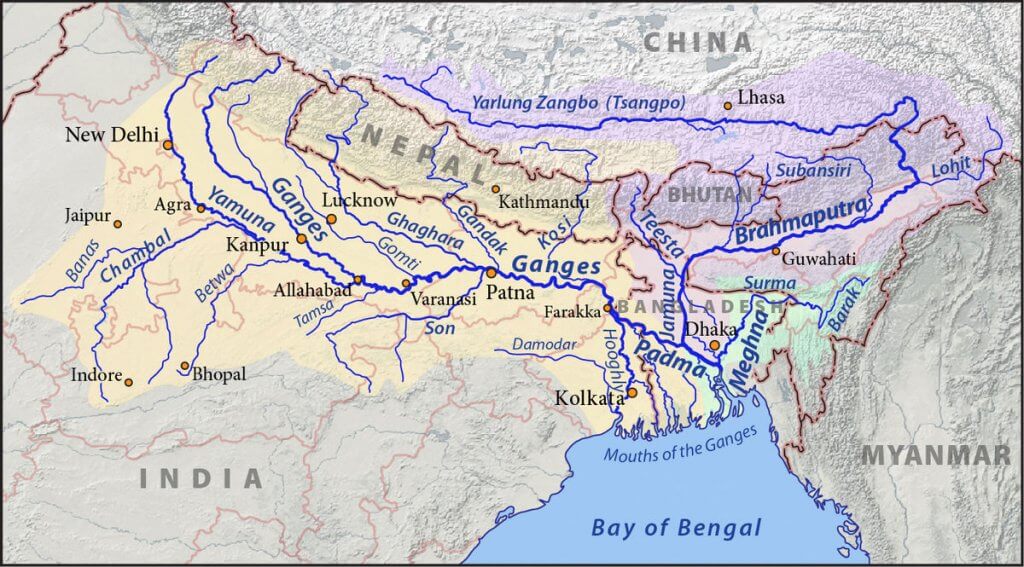
Ganga plains
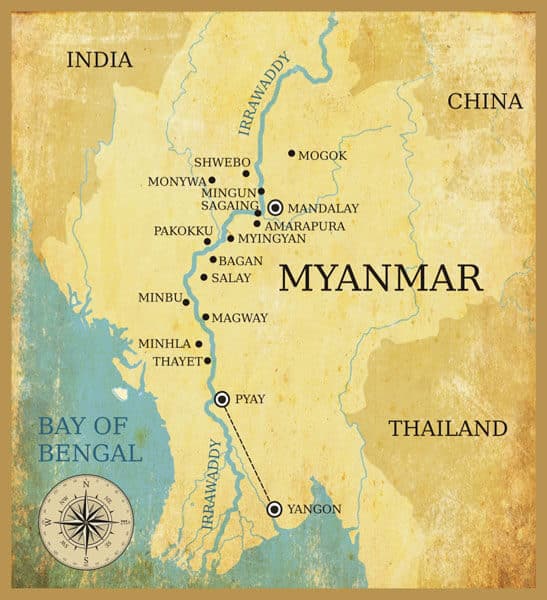
Irrawaddy plains
2. The Central Mountains
- These are the prominent and extensive mountain ranges that cover the parts of Central Asia.
- They consist of Pamir and Tian Shan ranges and extending across portions of Afghanistan, China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.
- These mountain ranges are designated as biodiversity hot spots by Conservation International which covers several montanes and alpine ecoregions of Central Asia.
- It encompasses several habitat types, including montane grasslands and shrublands, temperate coniferous forests, and alpine tundra.
- A mountain knot is a junction of two or more mountain ranges. The two main mountain knots in Asia are:
- The Pamir Knot is the junction of five mountain ranges they are the Sulaiman, the Hindu Kush, the Kunlun, the Karakoram, and the Himalayan ranges. Mount