Mineral Resources
A mineral is a naturally occurring substance, representable by a chemical formula, that is usually solid and inorganic, and has a crystal structure.
More than two thousand minerals have been identified and most of these are inorganic, which are formed by the various combination of elements. However, a small proportion of the earth’s crust contains organic materials, consist of single elements such as gold, silver, diamond, and sulfur.
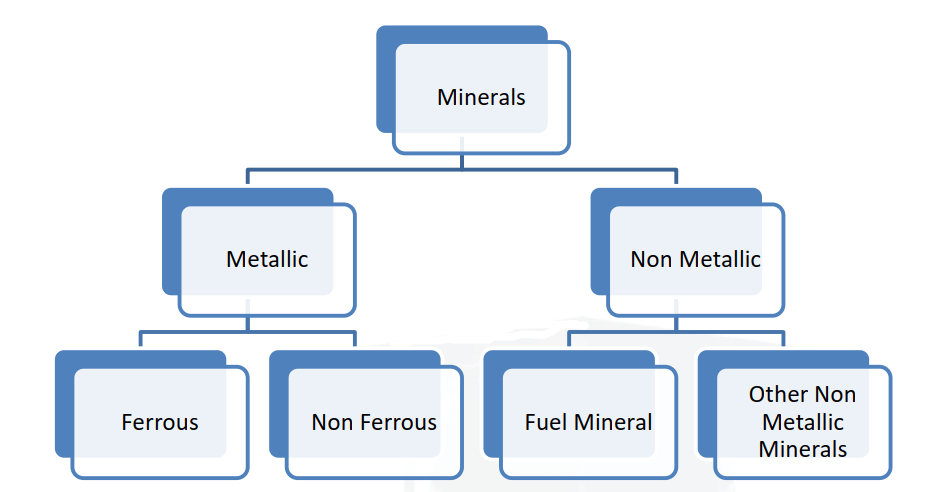
Mineral resources can be divided into two major categories.
- Metallic Mineral Resources
- Non-metallic Mineral Resources
Metallic Minerals
- Metallic Minerals are minerals in which metal elements are present in their raw form. When metallic minerals are melted a new product is formed.
- Metallic minerals constitute the second most important group of minerals after fossil fuels. They are reserved in Archean rocks.
- Major examples of metallic minerals are iron ore, copper, gold, Zink, Silver, Manganese, Chromites, etc. They constitute 7% of the total mineral value in India.
- These minerals provide a strong base for the development of the metallurgical industry, and thereby help the process of industrialization and urbanization. India has a substantial reserve of these minerals.
- Metallic minerals are further sub-divided as ferrous and non-ferrous metallic minerals
- The minerals containing iron are known as ferrous (Chromites, Iron ore, and manganese), and without iron are known as non-ferrous (lead, silver, gold, copper, bauxite, etc.).
- Significance of Metallic Mineral:
- the standard of living of the people living in a country is judged by the consumption of iron. It is the backbone of modern civilization and the foundation of basic industry.
Non-metallic Minerals
- Non-metallic minerals do not contain any metal substances in them. Nonmetallic minerals are a special group of chemical elements from which no new product can be generated if they are melted.
- Depending upon the origination, non-metallic minerals are either organic (such as fossil fuels also known as mineral fuels, which are derived from the buried animal and plant, e.g. such as coal and petroleum), or inorganic minerals, such as mica, limestone, graphite, etc.
| Metallic | Non-Metallic |
|---|---|
| Metallic Minerals are minerals in which metal elements are present in their raw form. | Non-metallic minerals do not contain any metal substances in them. |
| When metallic minerals are melted a new product is formed. | In the case of non-metallic minerals, you don’t get any new product after such a process. |
| Metallic minerals are usually found in igneous and metamorphic rock formations. | Non-metallic minerals are often found embedded in young fold mountains and sedimentary rocks. |
| Metallic minerals are good conductors of electricity as well as heat. | Non-metallic minerals are basically good insulators of electricity and heat. |
| Metallic minerals have high malleability and ductility. | Non-metallic minerals, lack in malleability and ductility, and these minerals break down easily. |
| Metallic minerals generally have lustre. | Non-metallic minerals do not have any shine or lustre. |
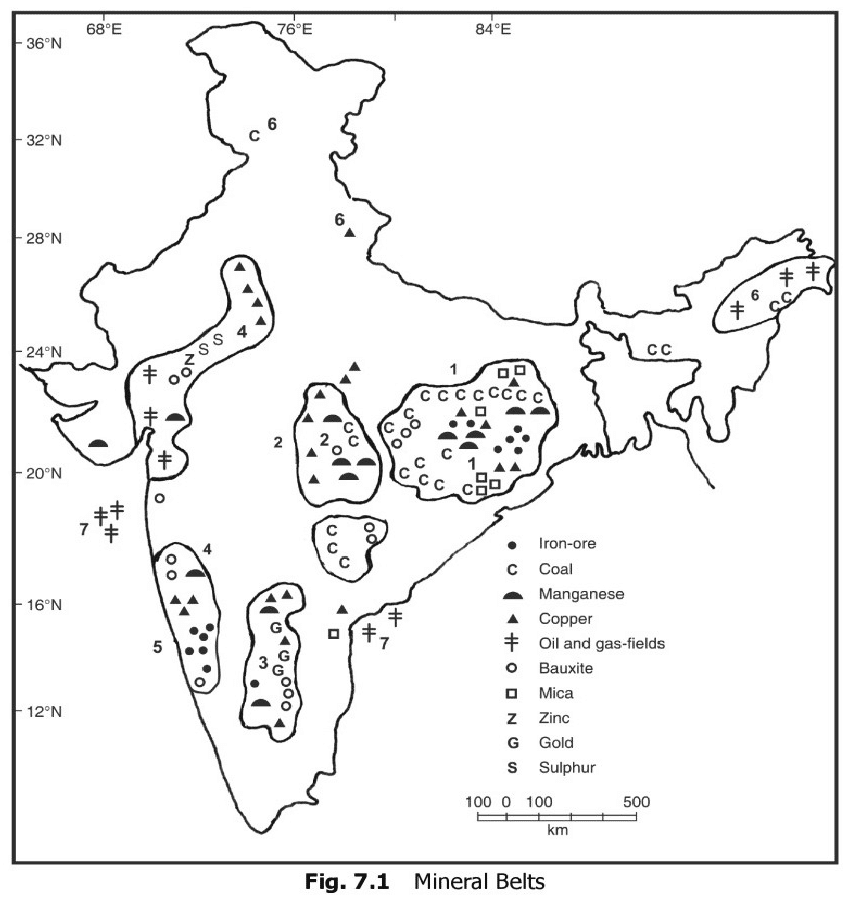
Mineral Resources in India (Mineral Rich Regions)
There are five major mineral belts in India namely:
- Northern Belt
- Central Belt
- Southern Eastern region
- South Western region
- North-Western region
Northern Belt: The Northern Belt comprise of the following regions-
- Chhota Nagpur plateau:
- Minerals found in this region is Kynite(100%), Iron (90%), Chromium(90%), Mica(75%), Coal(70%).
- Manganese, copper, and limestone are some other minerals found in this region.
- Assam Petroleum reserve: This region comprises the reserves of petroleum and lignite coal, tertiary coal, etc.
Central belt:
- This region comprises the Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra region which is the extension of the Chhota Nagpur plateau.
- There are huge reserves of Iron and limestone in Chhattisgarh.
- Godavari-Wardha valley with huge coal reserves lies in this region.
South Eastern region
- Eastern Karnataka: In this region, Bellary and Hospet are known for their iron reserves
- Andhra Pradesh: Cuddapa and Kurnool region are major mining centres. Nellore in Andhra Pradesh is known for Mica reserves.
- Telangana: Telangana is known for Bauxite reserves.
- Tamil Nadu: Tamil Nadu has the highest lignite coal reserves in India.
South Western region
- Karnataka:Dharwad region of Karnataka is known for its high mineral reserves.
- Shimoga, Chitradurg, Yumkur, Chikmaglur are some other areas with high mineral reserves.
- Goa is known for its rich iron reserves.
- Ratnagiri in Maharashtra also has iron reserves.
North Western region
- This region consists of the areas Rajasthan and Gujarat along the Aravalli Range.
- Gujarat is known for its petroleum deposits. Gujarat and Rajasthan both have rich sources of salt.
- Example: Salt from Kutchh and Playa Lake of Rajasthan.
- Rajasthan is rich in building stones i.e. sandstone, granite, marble. Gypsum and Fullers earth deposits are also extensive. Dolomite and limestone provide raw materials for the cement industry.