The Earth
- Earth is the only known planet where life exists.
- Its surface area is covered with two-third of water that is why we call it a blue planet.
- Earth is the third planet from the sun, the densest planet in the solar system, the largest of the solar system’s four terrestrial planets.
- In size, it is the fifth-largest planet. It is the largest terrestrial planet. The other terrestrial planets are Venus, Mars, and Mercury.
- It is slightly flattened at the poles, that is why its shape is described as a Geoid. Geoid means an earth-like shape.
- Earth revolves around the Sun, but its average distance from it is 149 million kilometers / 93 million miles. In astronomy, this is 1 AU – or an astronomical unit.
- Scientists have researched and estimated that our Earth is around 4.5 billion years old. Earth formed at around the same time as the rest of our Solar System.
- Earth revolves around the Sun once every 365.25 days – this is known as one Earth year.
- Only 3% of Earth’s water is fresh and 97% of it is salty.
- The surface of Earth is covered by water, around 71%, only 29% of Earth’s surface is covered by land.
- The atmosphere of Earth is divided into 6 layers – the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere, and ionosphere.
- Earth has only one satellite – the Moon, but it also has a couple of temporal artificial satellites.
Size and Shape of the Earth
- Earth is not perfect circle it is an oblate spheroid, it is like a sphere, but the distance from pole to pole is less than the distance around the equator (middle).
- The shape of the Earth is called “geoid” that is, ‘an Earth-like shape’.
- Earth is bulged out at equator and flattered at poles because of centrifugal force.
- The earth spins at constant rate but rate of movement is different the equator is moving fastest and poles are not moving (ignoring the fact that earth is orbiting the sun). Because of this movement centrifugal force is pulling matter closer to equator which structure outwards giving earth slightly non-spherical shape.
- Geodesy is the science that studies the shape and size of the Earth.
- Earth’s circumference and diameter differ because its shape is classified as an oblate spheroid or ellipsoid, instead of a true sphere. This means that instead of being of equal circumference in all areas, the poles are squished(slightly flattened at the North and South Poles), resulting in a bulge at the equator, and thus a larger circumference and diameter there.
- The equatorial bulge at Earth’s equator is measured at 26.5 miles (42.72 km) and is caused by the planet’s rotation and gravity.
Motions of the Earth
- Motion is the action or process of moving or of changing place or position.
- The Earth is constantly in motion, revolving around the Sun and rotating on its axis. These motions account for many of the phenomena we see as normal occurrences: night and day, changing of the seasons, and different climates in different regions.
- The earth has two movements, rotation and revolution.
- Rotation- A rotation is a circular movement of an object around a center (or point) of rotation.
- A three-dimensional object rotates always around an imaginary line called a rotation axis.
- If the axis is within the body, and passes through its center of mass the body is said to rotate upon it, or spin.
- Rotation causes days and nights. It takes 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4.09 seconds for a sidereal day and an exact 24 hours for a mean solar day.
- Earth rotates on its axis from west to east(counter-clockwise). The speed of Earth’s rotation is 1,674.4 km/h or 1,040.4 miles per hour at the equator.
- The earth has a 23.45° tilt of axis.
- While the Earth is spinning on its axis, it is revolving around the Sun in a counter-clockwise direction. It takes the Earth one full year to complete one full revolution around the Sun. This path is known as the Earth’s orbit. The mean distance of the Earth from the Sun is about 93 milling miles and the distance varies by 3 million miles, forming a slightly oval path.
- The revolution of the Earth around the Sun traverses a distance of 595 million miles in 365 days, 6 hours, 9 minutes, and 9.5 seconds. This means a speed of 18 miles a second (or 66,000 miles per hour) while at the same time rotating once each twenty-four hours.
Leap Year
- It takes approximately 365.25 days for Earth to orbit the Sun — a solar year.
- In an ordinary year, if you were to count all the days in a calendar from January to December, you’d count 365 days. But approximately every four years, February has 29 days instead of 28. So, there are 366 days in the year. This is called a leap year.
Earth rotates in an elliptical orbit around the Sun
- The orbit of the Earth around the sun is elliptical and not circular. Due to this, the distance between the Earth and the sun keeps changing.
- When this distance is minimum, the Earth is said to be in perihelion (around January 3), When the distance is the maximum, it is said to be in aphelion (around July 4).
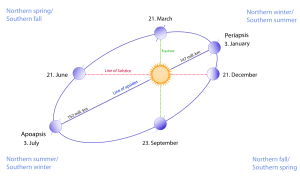
- The Earth’s axis points constantly to the same point (the polar star) in the celestial sphere.
- As a consequence, the latitude on the surface of the earth at which the sun’s rays fall vertically keeps changing as the earth moves its orbit around the sun. Due to this, the earth attains four critical positions with reference to the sun.
- Equinoxes: Equinox refers to a day with an equal duration of day and night. We have two equinoxes in a year which are:
- Spring equinox on March 20
- Autumnal equinox on September 22
- Solstice: On the other hand, solstice refers to a day with either the longest day or the shortest. The two solstices in a year are:
- Winter solstice on December 22
- Summer solstice on June 21
- Equinoxes: Equinox refers to a day with an equal duration of day and night. We have two equinoxes in a year which are:
| Equinox | Solstice |
|---|---|
| Time of the year when the sun is nearest to the equatorial plane giving equal lengths of day and night | Time of the year when the sun is farthest from the equatorial plane resulting in long nights and days |
| An equinox occurs at the start of the spring and fall | The solstice occurs during the summer and the winter |
| Happens twice a year | Happens twice a year |
| Occurs on March 20 (vernal equinox) and on September 22 (autumnal equinox) | Occurs on June 21(Summer Solstice) and on Dec 22 (Winter Solstice) |
Latitudes and Longitudes
Latitudes and Longitudes are imaginary lines used to determine the location of a place on earth.
Latitudes
- The Parallel of Latitudes extends from the Equator to 90 degrees North Pole and 90 degrees South Pole.
- If the latitude are drawn at an interval of 1 degree, then in each of the hemispheres there will be 89 latitude lines that will add up to 179 total lines.
- They are mainly the east-west circles that connect all the locations of the Earth.
- The distance between two parallel latitudes is 111km.
- All the latitudes are parallel to the Equator.
Major Parallel of Latitudes
Equator
- Equator is the imaginary line that divides the earth into two hemispheres.
- The northern hemisphere and the Southern hemisphere.
- It is the longest line of latitude.
- The Equator covers 40075km out of which 78.8% covers the water area while 21.3% covers the surface area.
Arctic Circle
- Out of the five parallel latitudes, Arctic Circle is the Northernmost circle which is at 66 and 1/2 degrees north of the Equator.
- The position of the Arctic is not always fixed.
- As per updates, the Arctic is drifting towards the North about 14.5 m (48 ft)/year.
- The Arctic Circle is 16000km long which covers 4% of the Earth’s surface.
Antarctic Circle
- Antarctic Circle is the Southernmost circle which is currently at 66 and a 1/2 degrees south of the Equator.
- Like the Arctic Circle, the Antarctic Circle is also shifting southward about 14.5 m (48 ft)/year.
- The Antarctic Circle is also 16000km long which covers 4% of the Earth’s surface towards the south.
Tropic of Cancer
- It is also known as Northern Tropic and the Sun is directly overhead at this position in June.
- The Tropic of Cancer is located at 23 and a 1/2 degrees in the Northern Hemisphere.
- The position of the tropic of cancer is fluctuating because of the longitudinal alignment. But the distance between the tropic of cancer and the Antarctic Circle remains the same as they move at the same speed.
- The length of the Tropic of Cancer is 36,788 km.
Tropic of Capricorn
- It is the Southern Tropic which is currently at 23 and a 1/2 degree south.
- The length of the Tropic of Capricorn is the same as the Tropic of Cancer.
- The Southern Tropic covers 3% of the total world’s population.
- The sun is overhead once a year in December and therefore experiences the maximum heat.